Game Theory Network Routing Projects addresses to provide sender-receiver data transmission in any wireless network. Game theory is an interactive model that makes the decision for complex systems too. As a matter of fact, routing plays the main role in network using which the data from one device reaches the other.
In truth, the game theory adapts to almost all the wireless networks. To be sure it is on sensor networks, that is to attain better performance. In this way, it improves the delivery ratio and, on the other hand, lows down energy usage. Hence the game theory allows designing a routing protocol that is robust.
Since the topic of routing is chief in a network, the game theory gains more attention. To this point, let us give you the three types in it such as cooperative, non-cooperative, and evolutionary. You can study it from our Game Theory Network Routing Projects. In detail, we give the info below.
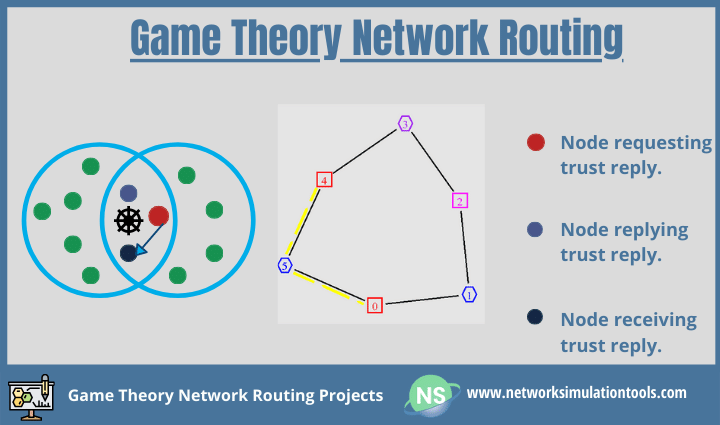
The five key terms to be in the note of Game Theory are 1. Players, 2. State, 3. Action, 4. Strategy, and 5. Equilibrium. Above all, the games are also of static, dynamic, zero-sum, and non-zero-sum & more. Even with, it prefers a route on the basis of a metric. The metric can be of any as underneath.
The game theory brings out prime choices for routing. Hence it is a type of optimization. At this time, the optimization combines with the game theory that is able to define one and multiple objectives. Hence the idea of this will be the best route selection in the network. To this end, the issues of game theory solve by anyone of the following method.
As we say above, the objective depends on network demands. In order to take corrective actions, the states of the player can be found from any one of the optimizations. Since the route between two nodes will transfer any type of data as sensing reports, live info, video, and so on with our PhD guidance in video streaming. If we define a strong objective, then the route will also assure for data transfer.
Whatever the network may be, it needs a single hop or multi-hop path. So far, the data from a node sent only through a route, and hence it is mandated. From here, the main networks are in the list below.
Beyond this, the game theory also offers to aid with the detection of fault, grouping, select ahead, and more. All in all, we help in all sorts of routing in networks. On the whole, we hope you gain a lot of ideas to work in this area. By still, it is hard while you work alone so that you can take our aid from start to the end.
| Technology | Ph.D | MS | M.Tech |
|---|---|---|---|
| NS2 | 75 | 117 | 95 |
| NS3 | 98 | 119 | 206 |
| OMNET++ | 103 | 95 | 87 |
| OPNET | 36 | 64 | 89 |
| QULANET | 30 | 76 | 60 |
| MININET | 71 | 62 | 74 |
| MATLAB | 96 | 185 | 180 |
| LTESIM | 38 | 32 | 16 |
| COOJA SIMULATOR | 35 | 67 | 28 |
| CONTIKI OS | 42 | 36 | 29 |
| GNS3 | 35 | 89 | 14 |
| NETSIM | 35 | 11 | 21 |
| EVE-NG | 4 | 8 | 9 |
| TRANS | 9 | 5 | 4 |
| PEERSIM | 8 | 8 | 12 |
| GLOMOSIM | 6 | 10 | 6 |
| RTOOL | 13 | 15 | 8 |
| KATHARA SHADOW | 9 | 8 | 9 |
| VNX and VNUML | 8 | 7 | 8 |
| WISTAR | 9 | 9 | 8 |
| CNET | 6 | 8 | 4 |
| ESCAPE | 8 | 7 | 9 |
| NETMIRAGE | 7 | 11 | 7 |
| BOSON NETSIM | 6 | 8 | 9 |
| VIRL | 9 | 9 | 8 |
| CISCO PACKET TRACER | 7 | 7 | 10 |
| SWAN | 9 | 19 | 5 |
| JAVASIM | 40 | 68 | 69 |
| SSFNET | 7 | 9 | 8 |
| TOSSIM | 5 | 7 | 4 |
| PSIM | 7 | 8 | 6 |
| PETRI NET | 4 | 6 | 4 |
| ONESIM | 5 | 10 | 5 |
| OPTISYSTEM | 32 | 64 | 24 |
| DIVERT | 4 | 9 | 8 |
| TINY OS | 19 | 27 | 17 |
| TRANS | 7 | 8 | 6 |
| OPENPANA | 8 | 9 | 9 |
| SECURE CRT | 7 | 8 | 7 |
| EXTENDSIM | 6 | 7 | 5 |
| CONSELF | 7 | 19 | 6 |
| ARENA | 5 | 12 | 9 |
| VENSIM | 8 | 10 | 7 |
| MARIONNET | 5 | 7 | 9 |
| NETKIT | 6 | 8 | 7 |
| GEOIP | 9 | 17 | 8 |
| REAL | 7 | 5 | 5 |
| NEST | 5 | 10 | 9 |
| PTOLEMY | 7 | 8 | 4 |